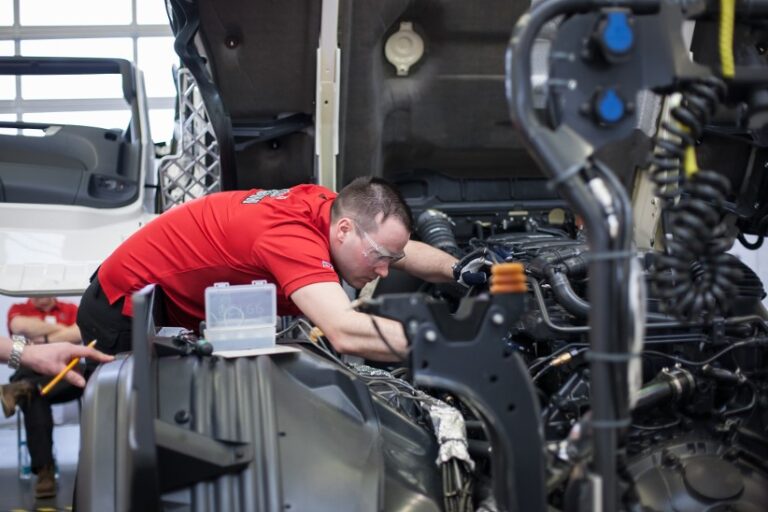
Scheduled and unscheduled maintenance are critical components of effective fleet management. For finance managers overseeing organisational budgets, understanding these forms of maintenance is pivotal. Maintenance can significantly impact both operational and capital budgets, affecting the overall financial health of a company. Furthermore, efficient maintenance is synonymous with risk mitigation and enhanced safety, emphasising its importance in fleet management.
A Proactive Approach to Fleet Management
Scheduled maintenance is a proactive approach to maintaining vehicles. It involves performing regular service, inspections, and repairs to prevent unforeseen breakdowns and ensure optimal vehicle performance. Examples include oil changes, tyre rotations, brake inspections, and fluid checks. By adhering to a regular maintenance schedule, fleet managers can ensure the longevity, reliability, and safety of the fleet, thereby reducing risks associated with vehicle breakdowns and accidents.
Financial Implications of Scheduled Maintenance:
From a financial standpoint, scheduled maintenance is a predictable expense and can be accurately budgeted for in advance. It aids in minimising unexpected and costly repairs, keeping operational costs in check. Additionally, regularly maintained vehicles often have higher resale values, positively affecting the capital budget. By incorporating scheduled maintenance into the annual budget, finance managers can allocate funds efficiently, ensuring that adequate resources are available to sustain fleet operationality and safety.
Addressing the Unpredictable
In contrast, unscheduled maintenance arises due to unforeseen issues and breakdowns, such as engine failure or accidents. Unlike scheduled maintenance, these are unplanned and can occur at inopportune times, leading to downtime and loss of productivity. Unscheduled maintenance can be a drain on operational budgets due to its unpredictability and, often, urgency.
Financial and Operational Impact of Unscheduled Maintenance:
Unscheduled maintenance poses a substantial financial risk, with the potential to disrupt budget allocations and constrain operational capabilities. These unplanned expenses can divert funds from other critical areas, stressing the operational budget. Further, the downtime associated with unscheduled maintenance can impact service delivery and operational productivity, potentially leading to loss of revenue and increased operational costs.
Moreover, the risk associated with unscheduled maintenance extends beyond financial concerns. A poorly maintained fleet can compromise safety, putting drivers and the public at risk. This can result in liability issues, potentially leading to substantial legal and compensation costs, tarnishing the organization’s reputation in the process.
Balancing the Budgets: A Strategic Approach
For finance managers, the goal is to balance operational and capital budgets effectively while ensuring the safety and efficiency of the fleet. Proactive fleet management strategies, including regular risk assessments and safety audits, can help in identifying and addressing potential issues before they escalate into costly repairs or safety hazards.
Investing in a robust fleet management system can aid in monitoring vehicle health, scheduling timely maintenance, and minimising unscheduled repairs. Furthermore, finance managers can benefit from allocating contingency funds in the budget to cover the costs associated with unforeseen maintenance, thus mitigating the financial strain on the operational budget.
The Role of Safety and Risk Mitigation
Safety is a paramount concern in fleet management. By emphasising preventative maintenance and addressing repair needs promptly, finance managers can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and breakdowns. This not only safeguards the well-being of the drivers and the public but also protects the organisation from potential legal ramifications and reputational damage.
Risk mitigation, encompassing both financial and safety considerations, is integral to effective fleet management. It involves identifying, assessing, and prioritising risks followed by coordinated application of resources to minimise, control, and monitor the impact of unforeseen events. Employing risk management strategies can aid in reducing unscheduled maintenance, fostering a culture of safety, and ensuring the fiscal well-being of the organisation.
In Summary
Scheduled and unscheduled maintenance are inherent aspects of fleet management, each with distinct implications for operational and capital budgets. For finance managers, comprehending the dynamics of these maintenance forms is crucial in formulating informed budgetary decisions and ensuring the uninterrupted functionality of the fleet.
Scheduled maintenance, with its predictability, aids in maintaining financial stability, promoting safety, and enhancing the longevity and reliability of the fleet. Unscheduled maintenance, conversely, can pose substantial financial and operational risks, necessitating proactive management and strategic budgeting to mitigate its impacts.
By prioritising safety, emphasising risk mitigation, and adopting a strategic approach to budgeting, finance managers can navigate the challenges posed by vehicle maintenance effectively, ensuring the sustained utilisation, safety, and financial health of their fleet.